Plant Extract Mediated Biogenic Synthesis and Characterization of Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles and its Environmental and Antibacterial Applications
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56946/jce.v2i2.280Keywords:
NiO NPs, nanoparticles, musa paradisiaca, antibacterial activity, chromium adsorption, MO degradation, MB degradationAbstract
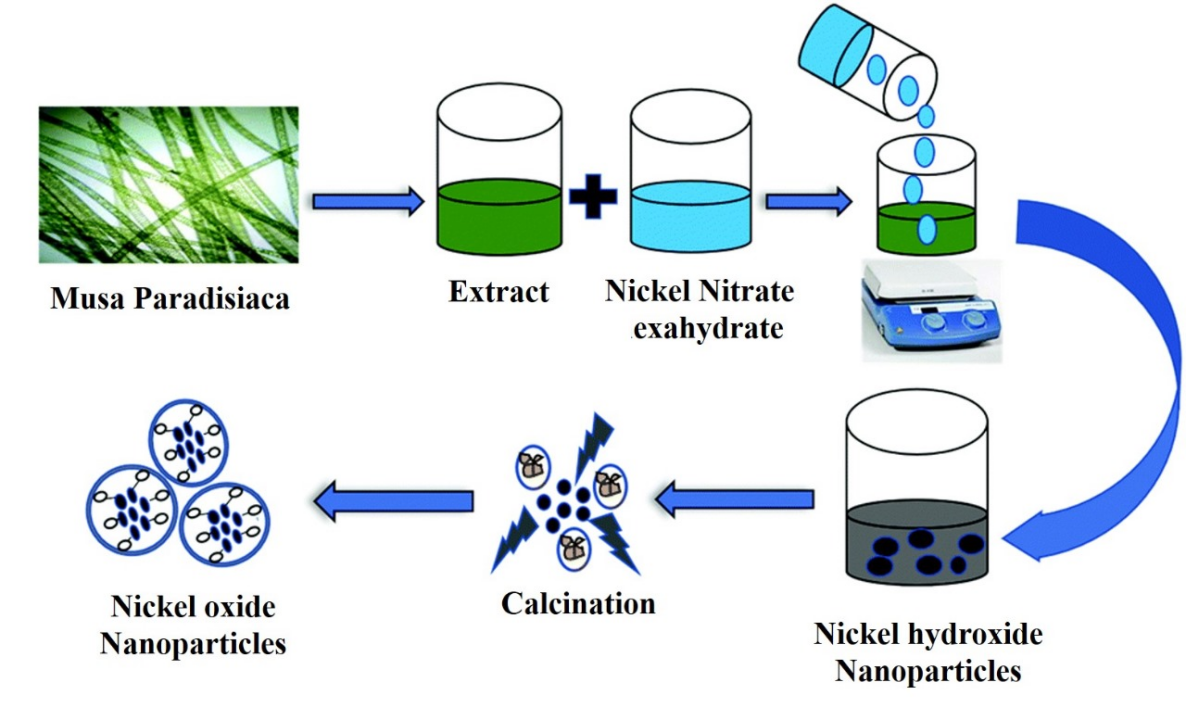
This research focuses on the green synthesis of Nickel Oxide nanoparticles (NiO NPs) using Musa paradisiaca, commonly known as banana plant, as a cost-effective and eco-friendly approach. Musa paradisiaca, utilized in traditional medicine, possesses various medicinal properties, including antioxidant, antibiotic, allogeneic, and hypoglycemic antimicrobial attributes. The peduncle extract of Musa paradisiaca serves as a reducing and capping agent for NiO nanoparticle synthesis. Characterization techniques such as XRD, EDX, and UV-vis spectroscopy were employed to analyze the properties of the synthesized NiO nanoparticles. XRD analysis confirmed an average grain size of 15.26nm, while SEM images revealed round cubic-shaped nanoparticles with a highly crystalline structure. The antibacterial activity of NiO nanoparticles was investigated against bacterial strains, including Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Bordetella bronchiectasis, and Bacillus subtilis, demonstrating effective antibacterial properties. Furthermore, the catalytic power of the synthesized nanoparticles was evaluated through the degradation of methyl blue and methyl orange dyes under sunlight and UV light. The results indicated superior degradation efficiency under sunlight compared to UV light for both dyes. Additionally, the study explored the adsorption activity of NiO nanoparticles for chromium (VI) at various concentrations, with the best adsorption percentage recorded at 17.23% under pH 4.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.


