Sources, Persistence, Ecotoxicology and Transformations of Anticancer Pharmaceutical Drug Residues in the Soil Environment: A Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.56946/jspae.v2i2.215Keywords:
Anticancer drugs, microbial transformation, drug degradation, soil biological health, soil qualityAbstract
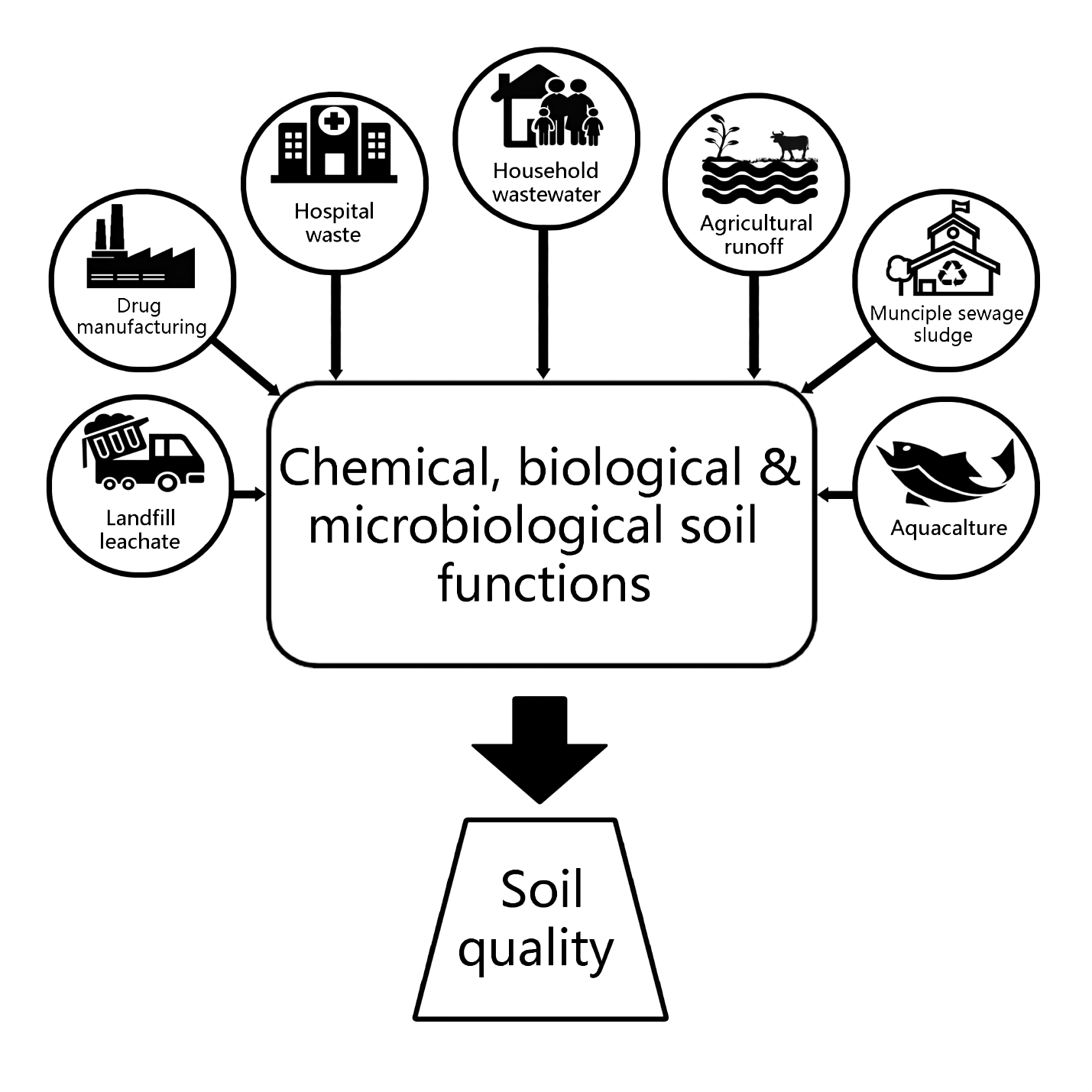
Release and environmental consequences of drug residues pose a major challenge for soil quality management. This review aims to synthesis the literature related to the transformations of anticancer drugs at the soil-water interphase and their ecological effects. Pharmaceutical drugs, including anticancer drugs originate form point and non-point sources of human and animal background. While detrimental effects of anticancer drug residues on human health are widely reported, a relatively little body of knowledge focuses on their persistence, decomposition and interaction with soil biological health and quality. Assessment of the potential ecotoxicological effect of the residues of anti-cancer drugs is far less frequent compared to other xenobiotics. However, a substantial concern is growing to understand the fate of these drug residues in the environment, particularly, under high environmental risk scenarios. Sewage sludge and hospital wastewaters are the primary sources of anticancer drug residues into the soil and their effects and transformations in soil depend on nature and persistence of drug residues. Depending upon their structure, anticancer drug residues can undergo biodegradation and biochemical transformations to form highly mobile molecules, which move into surface and ground waters, ultimately end up in the soil to alter microbial communities and their functions associated with flow of energy, nutrient cycling and ecosystem functions. This manuscript reviews the behavior of anticancer pharmaceutical residue in the soil environment in terms of effects on soil functions and quality by summarizing the limited available data.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
